Wild Salmon vs Farmed Salmon
Salmon is prized for its health benefits. This fatty fish is loaded with omega-3 fatty acids, which most people don’t get enough of.
However, not all salmon is created equal.
Let’s take a look at some differences between wild salmon vs farmed salmon and how to tell the difference between the two.
What’s the Difference Between Wild Salmon vs Farmed Salmon
Wild salmon is caught in natural environments such as oceans, rivers and lakes. But salmon is also farmed. In fact, farmed salmon now accounts for about 80% of the world’s salmon supply. The problem with that? Fish farms, which use a process known as aquaculture to breed fish for human consumption.
The biggest concern with farmed salmon is organic pollutants like PCBs. If you try to minimize your intake of toxins, you should avoid eating farmed salmon too frequently. Antibiotics in farmed salmon are also problematic, as they may increase the risk of antibiotic resistance in your gut.
Wild salmon eat other organisms found in their natural environment, whereas farmed salmon are given a processed, high-fat, high-protein feed in order to produce larger fish.
How can you tell the difference? When raw, a salmon filet will display white lines running across its flesh. This is fat. Wild salmon will generally not exhibit this build-up of fat between its muscles.
Differences in Nutritional Value
For this reason, the nutrient composition of wild and farmed salmon differs greatly. The table below provides a good comparison.
Calories, protein and fat are presented in absolute amounts, whereas vitamins and minerals are presented as percent (%) of the reference daily intake (RDI).
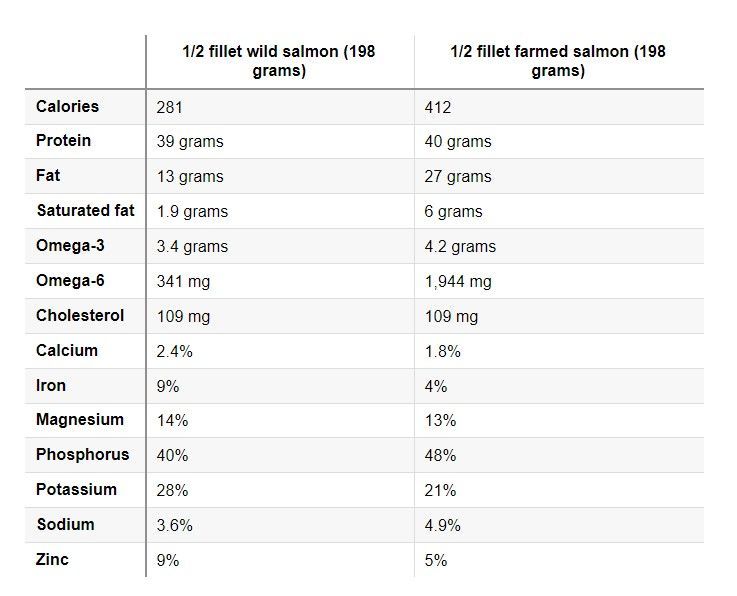
Clearly, nutritional differences between wild and farmed salmon can be significant.
- Farmed salmon is much higher in fat, containing slightly more omega-3s, much more omega-6 and three times the amount of saturated fat. It also has 46% more calories — mostly from fat.
- Compared to their farmed equivalents, wild salmon is richer in omega 3 fats and the carotenoids (which is what gives them their vibrant coral color). Wild salmon also contains more minerals.
- Farmed salmon is higher in vitamin C, saturated fat, polyunsaturated fatty acids and calories. The two main polyunsaturated fats are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These fatty acids play important roles in your body.
They’re termed essential fatty acids, or EFAs, because you need both in your diet.
View this post on Instagram
However, it’s necessary to strike the right balance.
Omegas
Most people today consume too much omega-6, distorting the delicate balance between these two fatty acids.
While farmed salmon has three times the total fat of wild salmon, a large part of these fats are omega-6 fatty acids. For this reason, the omega-3 to omega-6 ratio is about three times higher in farmed salmon than wild.
It’s also important to note that farmed fish tend to ingest more potentially harmful contaminants from the water they swim in and the foods they eat. Studies published in 2004 and 2005 showed that farmed salmon had much higher concentrations of contaminants than wild salmon.
Keep in mind that farmed salmon is still a healthy choice and provides healthy omega-3s. However, because of environmental and dietary differences, farmed salmon may contain more potentially harmful contaminants than wild salmon. While these contaminants appear to be safe for the average person consuming moderate amounts, some experts recommend that children and pregnant woman only eat wild-caught salmon — just to be on the safe side.
Budget may also play a factor in your choices. Wild salmon is also much more expensive than farmed and may not be worth the extra cost for some people. So, depending on your budget, it may be inconvenient or impossible to buy wild salmon.

The Bottom Line
Aim to eat fatty fish such as salmon 1–2 times per week for optimal health. This fish is delicious, loaded with beneficial nutrients and highly filling — and therefore weight-loss-friendly.
And, if your salmon comes in a package, remember to READ the ingredients list. Avoid products that have added dyes, sugar or have long lists of unpronounceable ingredients.
In the end, given its high amount of omega-3s, quality protein and beneficial nutrients, any type of salmon is still a healthy food.
Recipe: Cajun Salmon and Fruit Salsa
Next time you buy salmon fillets, try this recipe from PN ! The hint of spice paired with the sweet and refreshing salsa is sure to please your taste buds.
Ingredients

Prep Time: 10 minutes Cook Time: 20 minutes Yields: 2 servings
Directions
Begin by dicing up ingredients for the fruit salsa – mango, tomatoes, red onion, and cilantro. Put diced ingredients into a bowl and add the lime juice and a small pinch of salt.
Let sit.
Next, mix together all of the spices and coat each salmon on the flesh side. On a BBQ or stove-top grill (if stove top add 1 tbsp olive oil to the pan) – grill skin down for 15 minutes on low-medium heat, flip over and cook another 5 minutes. If the fish needs longer to cook – flip back to the skin side and continue cooking – it should no longer be pink inside.
Top fish with salsa and additional cilantro if desired.
Enjoy!
References: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16251623/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15506184/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15866762/
The post Wild Salmon vs Farmed Salmon appeared first on Salus.





